

The package allows the workflow to be executed on any R environment. rANOMALY is fully implemented in R language in which each step correspond to one function, allowing to easy implementation of new features or tools while being easy to use and maintain. Here we present rANOMALY, a scalable and lightweight R package which is able to handle every step of a metabarcoding analysis, from read cleaning, contaminant filtering, taxonomic assignment, to advanced statistical analysis.
#10 permute 5 software#
Methods and software are continuously evolving and the main challenge for bioinformaticians is to implement the most recent and effective ones in their analysis. Metabarcoding generates a large amount of data and a lot of applications already exist for their processing (FROGS 1, qiime 2). Studies of microbial communities tends to become a daily routine analysis for lots of laboratories and the main method to explore microbial diversity is metabarcoding, which is an amplicon targeted sequencing method (16S for bacteria and ITS for fungi).
#10 permute 5 code#
Our package produces ready to publish figures, and all of its outputs are made to be integrated in Rmarkdown code to produce automated reports. It integrates all assets of the latest bioinformatics methods, such as better sequence tracking, decontamination from control samples, use of multiple reference databases for taxonomic annotation, all main ecological analysis for which we propose advanced statistical tests, and a cross-validated differential analysis by four different methods.
#10 permute 5 install#
rANOMALY is an easy to install and customizable R package, that uses amplicon sequence variants (ASV) level for microbial community characterization. The main purpose of this package is to automate bioinformatic analysis, ensure reproducibility between projects, and to be flexible enough to quickly integrate new bioinformatic tools or statistical methods. This workflow is based on several R functions and performs automatic treatments from fastq sequence files to diversity and differential analysis with statistical validation. We present an R package for data analysis of 16S and ITS amplicons based sequencing.


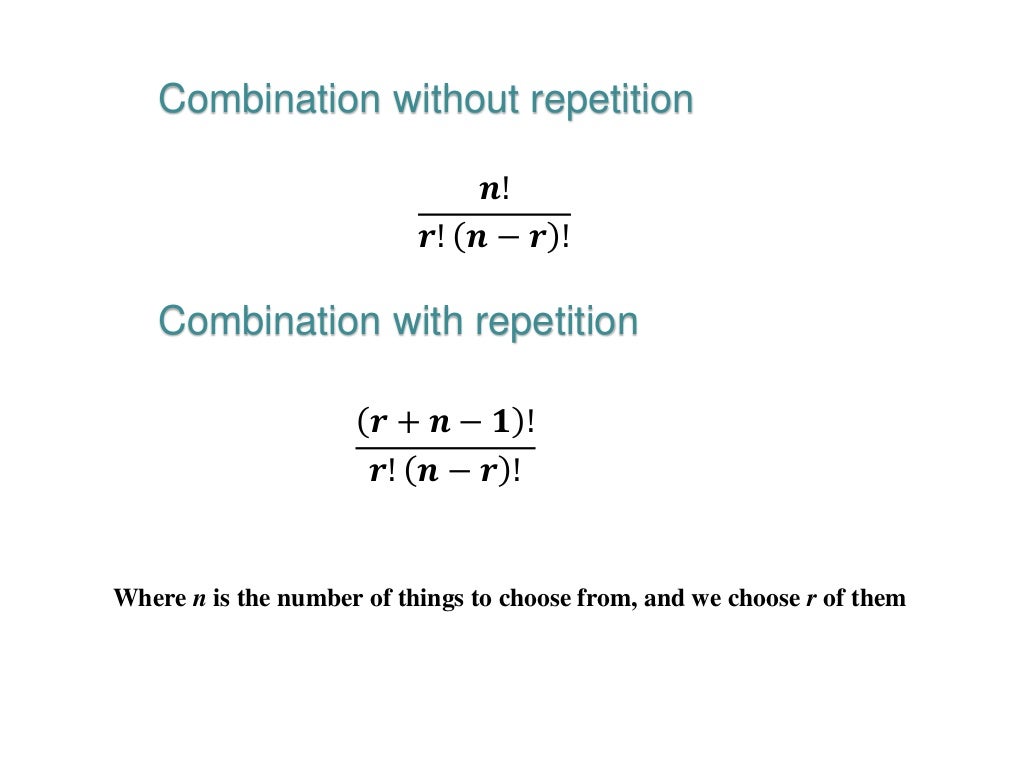
As the examples above illustrate, this can be used to better understand many different types of situations.Bioinformatic tools for marker gene sequencing data analysis are continuously and rapidly evolving, thus integrating most recent techniques and tools is challenging. What these two concepts have in common, is that they both help us understand the relationships between sets and the items or subsets that make up those sets. The most important difference between the two, however, is that combinations deal with arrangements in which the order of the items being arranged does not matter-such as combinations of pizza toppings-while permutations deal with arrangements in which the order the items being arranged does matter-such as setting the combination to a combination lock, which should really be called a permutation lock because the order of the input matters. Both combinations and permutations are used to calculate the number of possible combinations of things. Though these concepts are very similar, probability theory holds that they have some important differences. What are your chances of winning the lottery?Īll of these questions can be answered using two of the most fundamental concepts in probability: combinations and permutations. If there are 8 swimmers in a race, how many different sets of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd place winners could there be? Combinations and permutationsIf you have 2 types of crust, 4 types of toppings, and 3 types of cheese, how many different pizza combinations can you make?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
